What Types of Connectors Are Used in Medical Devices?
Medical devices of all sizes and types rely on connectors to ensure safe and reliable power delivery, data transfer, and fluid management. Many of these medical-grade connectors are rated for biocompatibility (ISO 10993), environmental sealing (IEC 60529), and electromagnetic interference (EMI) immunity (IEC 60601-1-2).
This article focuses on various medical connectors, such as implantable devices, card-edge solutions, and board-level interconnects. It also explores header pinouts, in-line options for board-to-board and wire-to-board integration, and spring-loaded connectors for wearable and portable medical devices. Finally, the article reviews widely used medical-grade connectors, including circular metal and quick-disconnect tubing.
Specialized Connectors for Implantable Medical Devices
As shown in Figure 1, implantable medical devices such as pacemakers, cochlear implants, and insulin pumps employ specialized connectors designed for long-term reliability, material compatibility, and high-performance operation.

Figure 1. Hermetic connectors feature gold plating, Kovar construction, and glass sintering sealing technology to enable high-reliability performance in medical implantable devices. Image credit: Sunkye
These connectors prevent contamination and enable essential functions, including power, data, and wireless communications. They also minimize EMI and resist external interference to maintain signal integrity. Key features include:
Hermetic Sealing: Provides airtight protection against pressure changes, moisture, and other environmental factors that can affect electrical connections.
Biocompatibility: Enables safe implantation and consistent operation of pacemakers and defibrillators. Most implantable cardiac devices meet the stringent standards of IS-1, DF-1, IS-4, and DF-4.
High-Density Micro: This technology supports miniaturized implantable devices by integrating power, data, and sensor transmission into a compact design without compromising performance.
RF Coaxial: Ensures efficient wireless communications by maintaining strong signal transmission with minimal interference.
Many of these connectors are made of durable medical-grade materials such as plastics, metals, ceramics, glass, and high-performance polymers such as PEEK and PEK. Some designs have insulation resistances of ≥5000 MΩ, leak rates of 1×10⁻³ Pa·cm³/s, and operating temperatures ranging from -40°C to 105°C. Notably, emerging micro-pad technology achieves electrical isolation of ~5 MΩ at 10 kHz, far exceeding traditional implant connectors.
Facilitating High-Speed Medical Data Transfer Using Card Edge Connectors
As shown in Figure 2, card edge connectors enable printed circuit boards (PCBs) with edge-mounted contact pads to be directly connected to other systems, facilitating high-speed data transfer and complex processing.
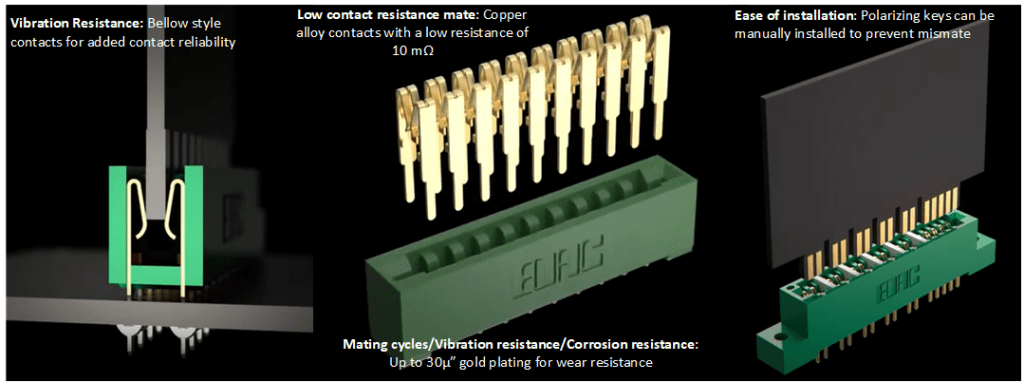
Figure 2. Card edge connectors feature bellows-style contacts for vibration resistance, copper alloy contacts for low resistance, and gold plating for wear resistance. (Image: ConnectorSupplier)
Data acquisition (DAQ) cards convert sensor data in blood analyzers through analog-to-digital (A/D) sampling systems. Similarly, advanced patient monitoring systems use card edge connectors to expand storage or test capabilities.
Medical-grade card edge connectors must meet stringent reliability standards. Frequent mating and unmating in high-vibration environments accelerates fretting corrosion and degrades contact surfaces, while reagent exposure further increases wear. Thicker gold plating prevents base metal oxidation, improves conductivity, and forms a protective barrier that minimizes material loss.
Enabling Reliable Board-to-Board and Wire-to-Board Connections
Manufactured from highly conductive copper alloys, header pin connectors are widely used in medical devices such as X-rays, CT scanners, ultrasound systems, and MRI machines. They also support diagnostic cardiology equipment, cardiopulmonary support systems, patient monitors, and blood analyzers.
Header pin connectors provide reliable board-to-board and wire-to-board connections by minimizing resistance and maintaining strong contact force. High-power headers support board-to-board power applications up to 20A, and integrated ground plane contacts improve electrical performance. For example, the 4 mm pin pitch minimizes the risk of arcing, ensuring safety in high-power medical systems.
While header pin connectors support board-to-board and wire-to-board connections, direct-plug connectors offer a more compact solution for wire-to-wire and wire-to-board applications, especially in medical harnesses. As shown in Figure 3, many medical header pin connector designs are fully sealed with epoxy protection to achieve IP67 dust protection and resistance to temporary liquid immersion in medical environments.
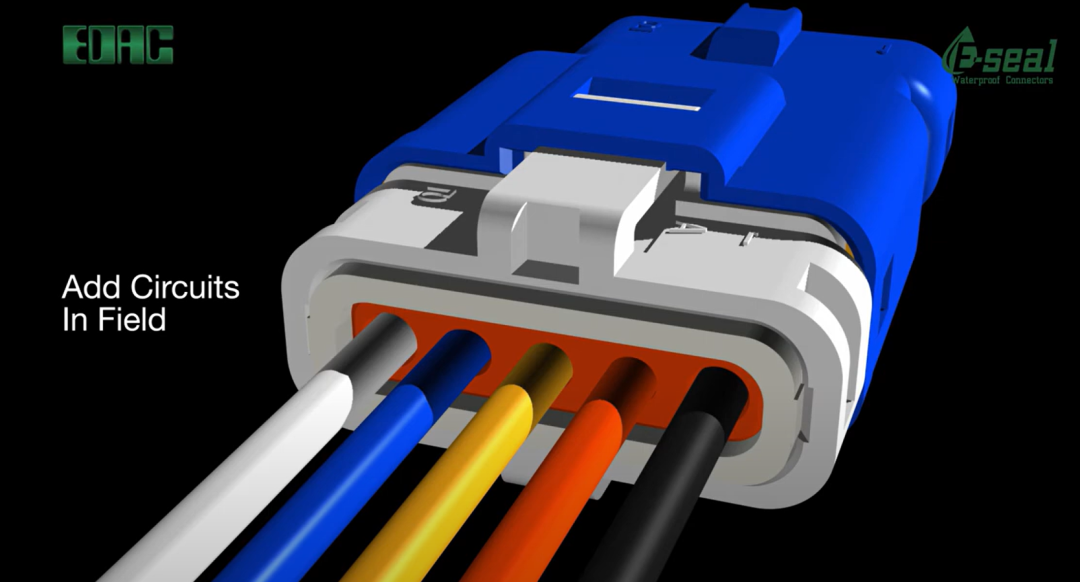
Figure 3. EDAC’s direct-plug connectors with E-Seal technology use a proprietary epoxy process that seals the entire back of the connector, rather than individual pins. This design is IP67 rated, provides dust protection, and resistance to temporary water immersion. Image credit: EDAC
Spring-loaded connectors for wearable and portable medical devices
Spring-loaded (pogo-pin) connectors help provide reliable charging and docking for wearable health monitors, portable medical devices, and home health devices. Many designs incorporate magnetic alignment for increased stability and ease of use. Rugged, IP-rated versions resist vibration and slight misalignment, ensuring continuous operation in compact applications such as hearing aids. Spring-loaded connectors maintain stable contact during turns, walking, and driving.
Medical-grade connectors for data, power, and fluid management
In addition to implantable and board-level connectors, a variety of medical-grade connectors help enable secure data transfer, reliable electrical connections, and efficient fluid management in critical medical applications. These include:
Quick-disconnect tubes: Figure 4 shows that these connectors enable safe, leak-free transfer of fluids and air. The valved mechanism seals when disconnected, preventing leaks and contamination, while the biocompatible materials and chemical-resistant seals withstand disinfectants, medications, and sterilization processes.
Circular metal: Circular metal provides a durable, high-reliability connection. The metal housing provides excellent EMI shielding, and IP68-rated sealing ensures sterilization resistance. Multiple keying options prevent misalignment, and high mating and unmating durability supports long-term use in harsh and demanding environments.
USB: USB facilitates data transfer and connectivity in patient monitoring systems, diagnostic equipment, and medical imaging devices. Medical-grade USB connectors feature rugged designs, waterproof seals, and secure locking mechanisms for additional durability.
HDMI: HDMI supports video display in medical imaging applications, such as bedside ultrasound. These systems require multiple video output options, including VGA, DVI, HDMI, and legacy formats such as S-video or C-video. Medical-grade HDMI connectors are designed for harsh environments and resist vibration, mechanical shock, and moisture. Its waterproof design features a protective seal to protect against splashes and resist corrosive substances.
D-sub: This connector supports sensor and actuator connectivity in medical monitors while ensuring robust electrical performance. Gold plating and secure mounting prevent contacts from degrading due to constant vibration, and specialized IP-rated sealing protects the D-sub from dust and moisture. Many connectors include metal housings that are grounded to the chassis and cable shield to minimize EMI and maintain signal integrity.
RF: This connector type transmits high-frequency signals in applications such as MRI machines, ultrasound equipment, and patient monitoring systems. It requires precise impedance matching and robust shielding to maintain signal integrity and prevent EMI. Medical-grade RF connector designs are also integrated into wearable devices to facilitate reliable wireless communications.
Conclusion
Medical-grade connectors support reliable power delivery, data transfer, and fluid management in implantable, wearable, and diagnostic devices. Advanced materials, precision engineering, and environmental sealing enable these connectors to withstand high vibration, frequent mating cycles, and harsh clinical and physiological conditions.
